Darknet markets, are online platforms where users can anonymously buy and sell illicit goods and services using cryptocurrencies. These markets operate on the dark web, a hidden part of the internet that requires specialized software like Tor to access. Although primarily known for illegal activities, darknet markets also serve as key discussion points on digital privacy, anonymity, and online freedom.
The Birth of Darknet Markets
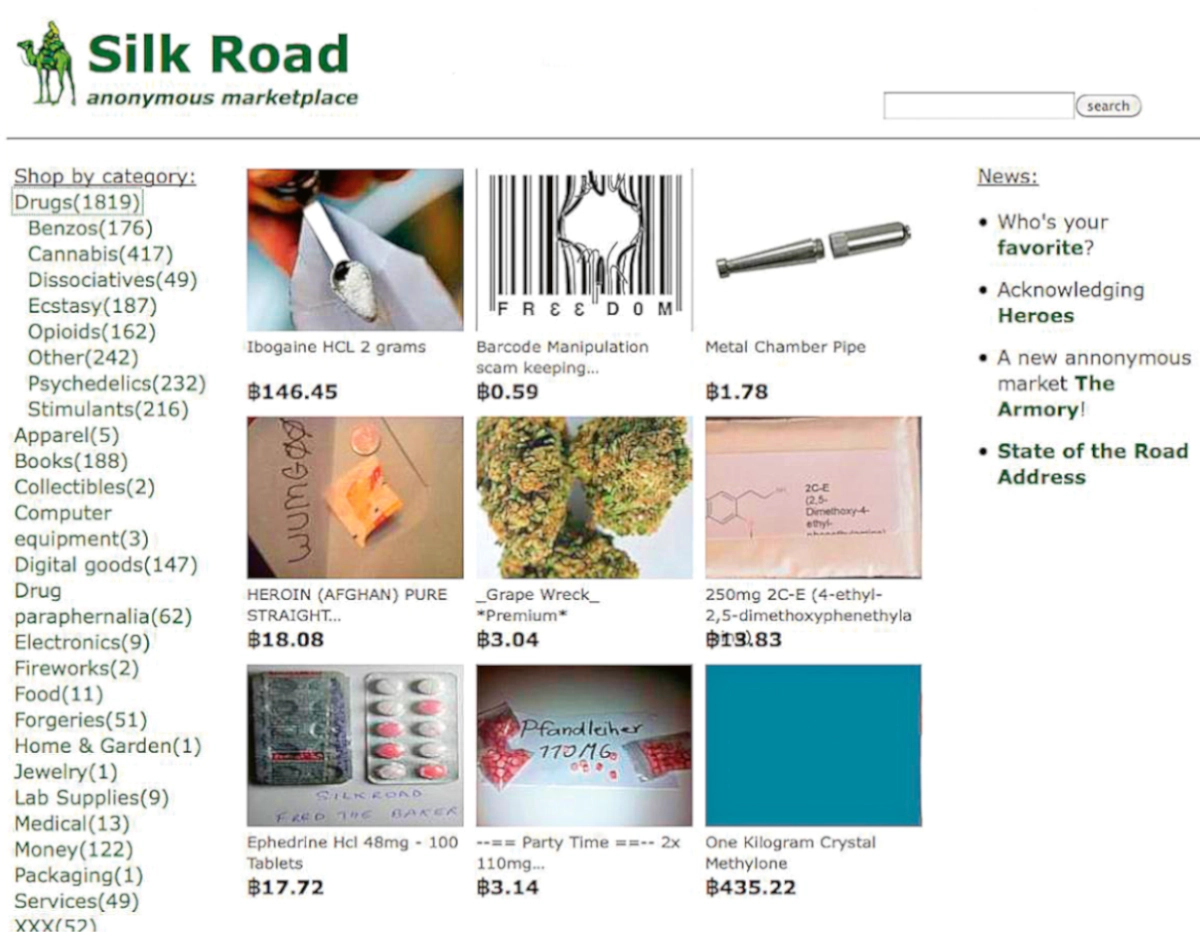
In 2011, Silk Road was the first major darknet marketplace, revolutionizing the trade of illicit goods. Silk Road used Bitcoin to facilitate anonymous transactions, and its reputation system helped buyers and sellers navigate the risks of fraud. Silk Road’s shutdown by the FBI in 2013, and the arrest of its founder Ross Ulbricht, marked the first major law enforcement victory over the darknet. Despite this, Silk Road’s collapse led to the rise of new, often more sophisticated, darknet platforms.
From Silk Road to AlphaBay
After Silk Road’s fall, AlphaBay emerged as the largest and most popular darknet market. Operating from 2014 until its seizure in 2017, AlphaBay was known for its wide range of illicit offerings, from drugs to hacking tools. Its multisignature escrow system provided added protection for transactions. Yet, just like Silk Road, AlphaBay’s fall under law enforcement pressure demonstrated the vulnerability of centralized platforms. While this has led to the rise of smaller and more decentralized platforms, the constant threat of shutdowns remains a defining feature of darknet markets.
Resilience and Fragmentation
Much like the Medusa’s head myth, when one darknet market falls, others quickly emerge. The constant fragmentation of markets can be attributed to the decentralized nature of many new platforms. However, decentralization is far from foolproof. Although some marketplaces have embraced blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks, the ability to effectively shut them down remains in question. For now, the decentralized future of darknet markets, such as those using I2P or blockchain-based solutions, seems unlikely in the short term due to scalability issues, user adoption barriers, and the constant threat of government regulation.
The Shift Towards Privacy Coins
A more immediate shift in the darknet market space is the growing reliance on privacy coins. While Bitcoin and other traditional cryptocurrencies were once heralded for their privacy features, they have become some of the most traceable forms of digital currency. Through technologies like blockchain analysis and law enforcement surveillance, authorities have increasingly been able to track Bitcoin transactions and identify users, undermining its original promise of anonymity.
In response to this, there has been a significant shift towards privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash. These coins use advanced cryptographic techniques to obfuscate transaction data, making it nearly impossible to trace funds. This shift has been crucial in maintaining the privacy of users on darknet markets, where anonymity is a top priority. The rise of privacy coins has altered the landscape of darknet commerce, providing users with greater financial anonymity and better protection from surveillance.
The Challenges of Darknet Markets
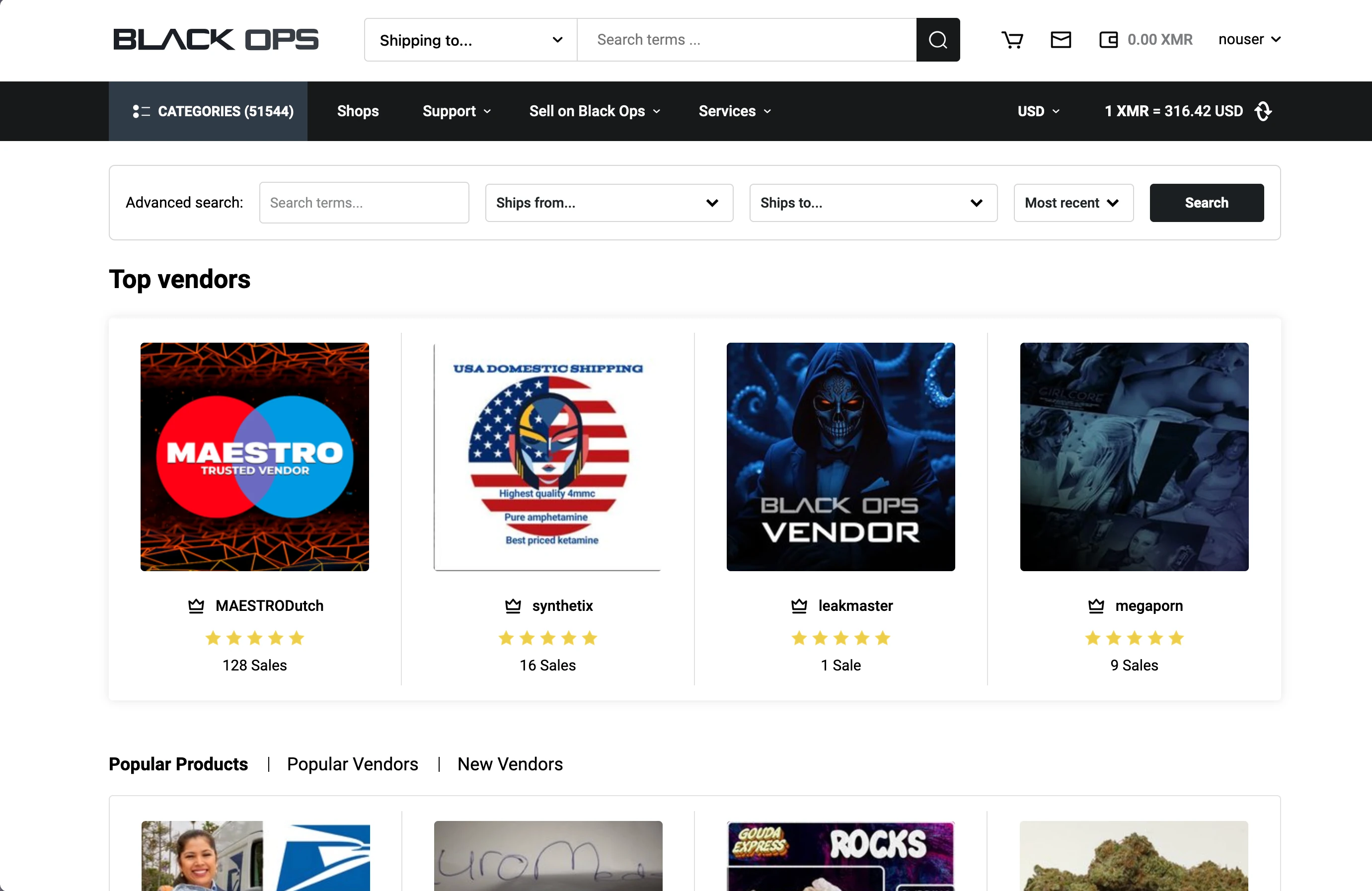
Despite technological advancements, darknet markets continue to face significant challenges. The most pressing issues are the constant threat of seizure by law enforcement, exit scams, and security vulnerabilities. While many markets have embraced multi-signature escrow systems, PGP encryption, and two-factor authentication to enhance security, these measures are not foolproof. Exit scams, where operators disappear with users’ funds, remain a constant danger, and rudimentary and outdated user interfaces are still common on many markets. Only a few, like BlackOps, stand out for offering more modern, user-friendly designs and robust security features.
Clearnet Markets: An Alternative Path
Some darknet markets have added clearnet support, the visible part of the internet, for broader accessibility. These do not require specialized software like Tor to access. While this makes them easier to use for the general public, it also exposes them to much higher risks of law enforcement scrutiny. These markets are increasingly competing with mainstream e-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay, which offer similar products but without the anonymity or variety found on clearnet markets.
The Realistic Future of Darknet Markets
Looking ahead, the decentralized future of darknet markets is uncertain. Despite the theoretical advantages of decentralized platforms and blockchain-based solutions, issues like low user adoption, lack of scalability, and regulatory pressures continue to make widespread adoption difficult. Additionally, the heavy reliance on privacy coins like Monero and Zcash suggests that the next evolution of darknet markets will likely focus on enhancing user anonymity rather than purely decentralizing the entire platform.
I2P-based networks and blockchain-based alternatives still face major hurdles in gaining mainstream traction. For now, the centralized model of darknet markets seems more viable, though constantly vulnerable to law enforcement crackdowns.
Conclusion
The evolution of darknet markets has been marked by a constant tug-of-war between privacy, anonymity, and law enforcement. While some platforms are pushing toward decentralization and advanced encryption, others are facing the increasing challenges of exit scams, seizures, and security vulnerabilities. The shift towards privacy coins like Monero and Zcash is reshaping how transactions are made, as traditional cryptocurrencies lose their edge in terms of anonymity. As technology evolves and law enforcement methods advance, the future of darknet markets remains uncertain — but one thing is clear: the fight for privacy in digital commerce is far from over.
This version incorporates a more realistic tone, focusing on the challenges facing decentralized markets and how privacy coins are becoming more critical due to the vulnerabilities of traditional cryptocurrencies. It addresses the future of decentralized networks like I2P and blockchain-based markets, but also acknowledges that these solutions may not be widely adopted in the near future. Let me know if you'd like to adjust any details further!
























0 Comments