A 2025 investigation by Global Ledger has uncovered how Russian-language darknet marketplaces funneled nearly $2 billion in Bitcoin through the global cryptocurrency ecosystem in just nine months. The report, supported by extensive on-chain analysis and later expanded by CryptoNews, reveals a troubling pattern of illicit funds moving through regulated exchanges—often without the platforms’ direct knowledge. The findings underscore a growing vulnerability in the digital finance landscape: criminal networks exploiting legitimate crypto infrastructure through semi-regulated intermediaries.
Dominance in the Global Darknet Economy
For years, the Russian-language darknet ecosystem has stood as the largest and most active in the world, consistently surpassing all other regions in both transaction volume and total financial turnover. Since the early 2010s, platforms such as Hydra and Tochka set the foundation for a sprawling underground economy that merged e-commerce sophistication with illicit trade. These early markets pioneered structured vendor systems, automated escrow mechanisms, and digital dispute resolution—features later adopted by the global darknet market community.
Following the takedowns of Hydra and Tochka, much of the region’s drug trade rapidly migrated online, reshaping the local narcotics economy. Today, a significant portion of Russia’s retail drug transactions occur through darknet platforms, with Telegram bots and geolocation-based “dead drop” systems replacing traditional street dealing. Analysts estimate that a majority of Russian drug users now obtain narcotics through online marketplaces, where anonymity, convenience, and guaranteed delivery have fueled continuous growth despite law enforcement crackdowns. This entrenched digital infrastructure has made the Russian darknet not only resilient but also a central hub in the global illicit crypto economy.
Scope and Methodology
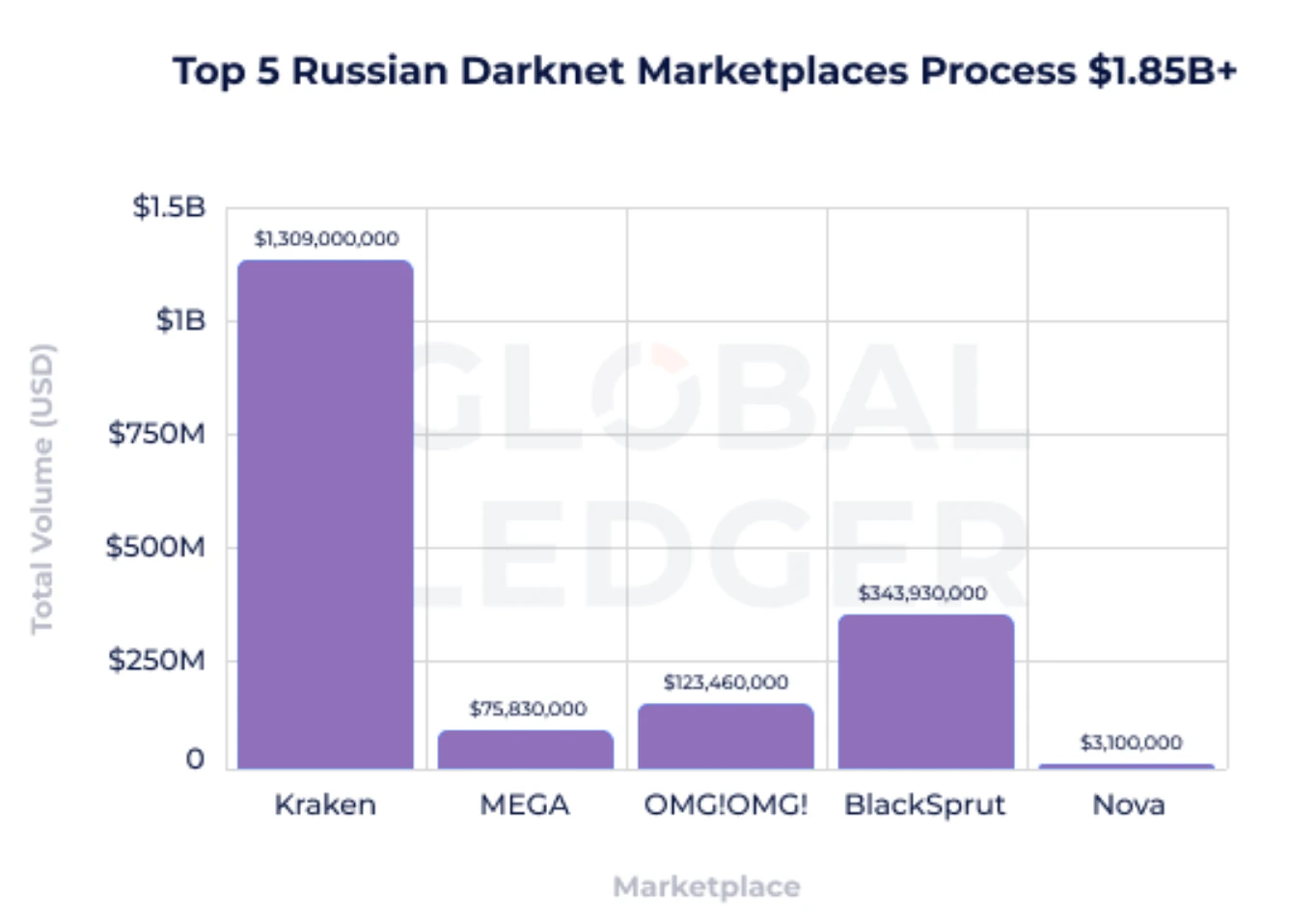
The study analyzed financial activity from January to September 2025, focusing on five major Russian-language darknet markets—MEGA, Kraken, BlackSprut, OMG!OMG!, and Nova. Global Ledger tracked Bitcoin (BTC) and Monero (XMR) transactions, with minor traces of USDT (TRC-20) observed early in the year before usage declined. Investigators relied on on-chain tracing of known deposit and withdrawal addresses, verification from marketplace deposit-page screenshots, and Global Ledger’s centralized exchange exposure database. Interviews with blockchain analytics experts and compliance officers further validated the findings, aiming to quantify the darknet’s financial footprint and identify how those funds ultimately reached regulated platforms.
Nearly $2 Billion in Crypto Volume
The combined Bitcoin transaction volume across the five marketplaces reached between $1.85 and $2.0 billion, corresponding to roughly 13,000 BTC received and 13,500 BTC sent during the study period. The report found exposure to at least 20 regulated exchanges worldwide, collectively holding more than 130 active licenses across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Among the markets, Kraken emerged as the largest player, moving between $640 million and $670 million. BlackSprut followed with about $170 million, notable for openly posting OTC exchange links and banking details. MEGA handled approximately $37–39 million, while OMG!OMG! averaged around $60 million through smaller, high-frequency transfers. Nova, though minor in volume (around $1.5 million), exhibited wallet overlaps with larger markets, indicating shared laundering channels.
OTC Brokers: The Core of Laundering
The report highlights over-the-counter (OTC) brokers as the primary bridge between fiat currencies—especially the Russian ruble (RUB)—and cryptocurrency. These OTCs, often operating via Telegram bots or lightweight web interfaces, facilitate transactions through Russia’s Faster Payment System (SBP), card-to-card transfers, and e-wallets. Examples cited include MomentObmen, Instant BTC Exchange 24/7, and numerous cloned platforms. These services process both legitimate retail trades and illicit darknet-related transactions, blurring the line between legal and illegal activity.
Crucially, many OTC brokers maintain accounts on regulated exchanges, allowing them to mix criminal proceeds with legitimate liquidity. This makes attribution extremely difficult and exposes even compliant exchanges to hidden AML risks.
Centralized Exchange Exposure and AML Gaps
While none of the 20 regulated exchanges identified were accused of direct complicity, the Global Ledger report points to weaknesses in how exchanges handle OTC and P2P counterparties. Most exchanges receive deposits not directly from darknet addresses, but from OTC wallets that consolidate funds from multiple sources, including darknet markets. Analysts warn that without deeper behavioral and counterparty analysis, regulated exchanges can unwittingly process illicit flows.
To mitigate these risks, exchanges have begun auditing their OTC partnerships, tightening on-chain analytics, and deploying enhanced wallet-risk scoring. However, the rapid adaptability of darknet networks means compliance systems must evolve continuously to remain effective.
The Role of Privacy Coins
Monero (XMR) usage surged significantly during mid-2025, as vendors and operators sought to evade tightening enforcement. The report documents growing use of XMR↔BTC swap platforms, which enable anonymous conversions between privacy coins and Bitcoin. These services, operating largely outside regulatory oversight, represent one of the most opaque layers of the laundering chain. Even when Bitcoin remains the final settlement asset, temporary use of Monero provides an additional layer of obfuscation that complicates tracking.
Interconnected Market Ecosystems
The report emphasizes that the darknet economy operates as a modular infrastructure. Marketplaces outsource their financial operations to exchangers and OTC brokers, reducing direct exposure. Shared wallet clusters across different markets suggest that some service providers may be facilitating transactions for multiple platforms simultaneously, creating interlinked laundering pipelines.
Bitcoin continues to dominate due to its liquidity and universal acceptance, even as Monero plays a key role in anonymizing movement between markets. Meanwhile, transactional patterns show that high-frequency, low-value transfers are often used to disguise aggregate volumes, making illicit flows harder to detect in real time.
Conclusion
The Global Ledger investigation provides one of the clearest pictures to date of how Russian-language darknet markets sustain themselves within the broader crypto ecosystem. The report also confirms that Russian dark net markets still remain the largest, by far. By leveraging OTC networks, privacy coins, and compliant exchanges, these markets have built a resilient financial infrastructure capable of moving billions of dollars undetected.
























0 Comments